 Real life example
Real life example
Different practical conditions are illustrated below along with relevant formulae.
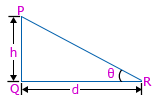
(i). Say, the angle of elevation of a tower from a distance 'd' from its foot is 'θ' and height of the tower is 'h' meter(refer ΔPQR). Then
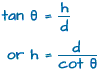
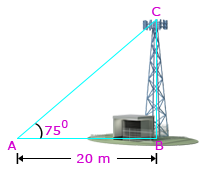
- Example: A cell tower stands vertically on the ground. From a point on the ground which is 20 m away from the foot of the tower, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is found to be 75°. Find the height of the tower.
Sol: Let height of the tower is BC.
Distance between foot of the tower and the observation point is AB.
From ΔABC, tan 75° = BC/AB
2 + √3 = BC/20
BC = 20(2 + √3)
∴ Height of the cell tower = 20(2 + √3) m.