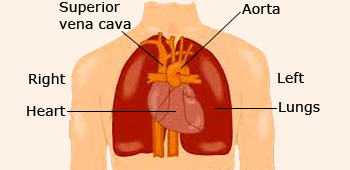
 Location of the heart in the thorax
The heart is located in the chest between the lungs behind the sternum and above the diaphragm. It is surrounded by the pericardium. Its size is about that of a fist, and its weight is about 250–300 g. Its center is located about 1.5 cm to the left of the midsagittal plane. Located above the heart are the great vessels: the superior and inferior vena cava, the pulmonary artery and vein, as well as the aorta. The aortic arch lies behind the heart. The esophagus and the spine lie further behind the heart.
Location of the heart in the thorax
The heart is located in the chest between the lungs behind the sternum and above the diaphragm. It is surrounded by the pericardium. Its size is about that of a fist, and its weight is about 250–300 g. Its center is located about 1.5 cm to the left of the midsagittal plane. Located above the heart are the great vessels: the superior and inferior vena cava, the pulmonary artery and vein, as well as the aorta. The aortic arch lies behind the heart. The esophagus and the spine lie further behind the heart.
The heart, which is about the size of your fist ‐ 12 cm in length and 9 cm in width, is an incredibly efficient organ that works constantly without ever pausing to rest.
Heart is located, right in the centre between the two lungs and above the diaphragm and is made of a unique cardiac muscle. The narrow end of the roughly triangular heart is pointed to the left side and during working, the contraction of the heart is most powerful at this end giving a feeling of the heart being on the left side.
The average weight of a female human heart is 9 ounces and a male's heart is 10.5 ounces. The heart comprises less than 0.5 percent of the total body weight. The heart has three layers. The smooth, inside lining of the heart is called the endocardium. The middle layer of heart muscle is called the myocardium.
It is surrounded by a fluid filled sac with a double walled membranous covering called the pericardium which protects the heart from mechanical injuries, while the lubricating pericardial fluid reduces friction during heart beat.