 Kidneys- Filtration units of our body
The kidneys maintain water volume and balance as well as regulate blood composition.
Kidneys- Filtration units of our body
The kidneys maintain water volume and balance as well as regulate blood composition.
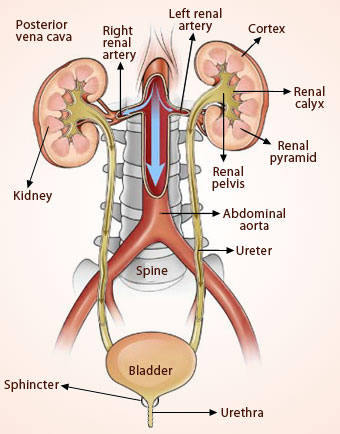
Kidneys are two bean – shaped organs, each about the size of your fist,10 cm long and 6 cm wide, located on either side of the backbone, just below the rib cage and protected by the last two ribs. Kidneys weigh about 0.5 percent of total body weight. The right side kidney is at a slightly lower level than the left one. Kidneys receive the blood from the renal artery, process it, return the processed blood to the body through the renal vein and remove the wastes and other unwanted substances in the urine.
A tube, the ureter, arises from the notch (hilum) in the median surface of each kidney and connects behind with the urinary bladder in the lower part of the abdomen. The front end of the ureter is somewhat expanded into the kidney and is called the pelvis. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. In the bladder, the urine is stored until it is excreted from the body through the urethra. The kidney is the only organ of the body in which two capillary beds, in series, connect arteries with veins. This arrangement is important for maintaining a constant blood flow through and around the nephron despite fluctuations in systemic blood pressure.
Structure of Kidney:
A longitudinal section of the kidney shows the following parts:
- Renal capsule: a thin, outer membrane that helps protect the kidney.
- Cortex: a lightly colored outer region.
- Medulla: a darker, reddish – brown, inner region composed of a finely striped substance arranged in several pyramids. The apex of each pyramid (papilla) projects into the pelvis of the kidney.
- Renal pelvis: a flat, funnel shaped cavity that collects the urine into the ureters.