 Hormones are responsible for chemical coordination in the body
Endocrine system consists of several glands/glandular cells which bring about the overall common function of chemical coordination in the body.
Hormones are responsible for chemical coordination in the body
Endocrine system consists of several glands/glandular cells which bring about the overall common function of chemical coordination in the body.
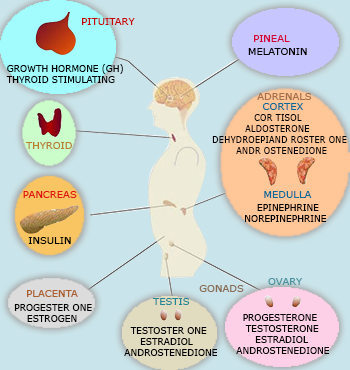
Hormones are secretions from specific cells or glands in the body and are carried to all parts by the blood and act as chemical signals to regulatory messages within the body. Most hormones are secreted by special glands, like thyroid and pituitary glands called the endocrine glands (endo: inside, crine: secrete) meaning “secrete internally”. They are also called ductless glands because their secretions are poured directly into the blood and not through any special duct.
Certain hormones are also produced from some such glands or other body parts which otherwise have a different primary function; for example, the stomach and duodenum. Hormones are also produced from living cells in an organ such as the beta cells of pancreas which produce insulin and Leydig cells of testis which produce testosterone. Hormone–secreting cells are present in many organs including the heart, thymus, liver, stomach, small intestine, kidney and placenta.
Hormone is a product of living cell that circulates in the body fluids to all parts away from its point of origin but produces a specific effect on the activity of the cells of the target organs only. A hormone may reach all parts of the body, but only certain types of cells, the target cells, are equipped to respond. Thus, a given hormone traveling in the bloodstream elicits specific responses such as a change in metabolism from its target cells, while other cell types are unaffected by that particular hormone. Endocrine glands act in a coordinated manner, activate each other and work as a system of organs called endocrine system.
A system is defined as a complex of organs performing an overall common function. Endocrine system consists of several glands/glandular cells which bring about the overall common function of chemical coordination in the body. The nervous system and endocrine system work in conjunction and some times it is difficult to distinguish them. A part of the brain called the hypothalamus contains neurosecretory cells which release hormones into the blood. The hormones produced by neurosecretory cells are sometimes called neurohormones to distinguish them from the “classic” hormones released by endocrine glands .