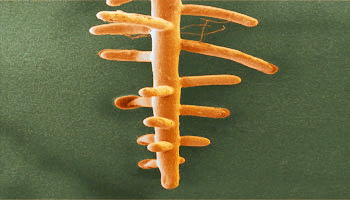
 Mycorrhiza- Fungal roots
A mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between a soil fungus and the roots of a vascular plant. The majority of vascular plants roots are mycorrhizal. Here fungal hyphae (thin threads, orange) are seen on the surface of the root. Both organisms benefit from this association. The fungus is able to access nutrient forms unavailable to the plant, process them and pass them on to the roots. The mass of hyphae also provide a large surface area for uptake of water and minerals. The fungus receives carbon compounds that the plant produces via photosynthesis.
Mycorrhiza- Fungal roots
A mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between a soil fungus and the roots of a vascular plant. The majority of vascular plants roots are mycorrhizal. Here fungal hyphae (thin threads, orange) are seen on the surface of the root. Both organisms benefit from this association. The fungus is able to access nutrient forms unavailable to the plant, process them and pass them on to the roots. The mass of hyphae also provide a large surface area for uptake of water and minerals. The fungus receives carbon compounds that the plant produces via photosynthesis.
Fungi are not only diverse and widespread, but they are also essential for the well-being of most terrestrial ecosystems. They breakdown organic material and recycle nutrients , allowing other organisms to assimilate essential chemical elements. Almost all plants depend on a symbiotic relationship with fungi that helps their roots absorb minerals from the soil. Humans also benefit from fungal services to agriculture and forestry as well as their essential role in making products ranging from bread to antibiotics. But it is also true that a tiny fraction of fungi causes diseases in plants and animals.
Blue–green patches on the surface of a rotting orange; grayish–white patches on stale bread, old pickles and jams; greenish patches during the rainy season on old shoes and damp shoes are all made of different types of fungi (Latin fungus, meaning “mushroom”).
Nearly one lakh species of fungi have been described till now and this wide diversity has enabled fungi to colonize in every terrestrial habitat. Fungi are not only diverse and widespread, but they are also essential for the well–being of most terrestrial ecosystems. Fungi break down organic material and recycle nutrients, allowing other organisms to assimilate essential chemical elements. Almost all plants depend on a symbiotic relationship with fungi that helps their roots absorb minerals from the soil.
Fungi play an essential role in making products ranging from bread to antibiotics. A tiny fraction of fungi causes diseases in plants and animals. Fungi are often classified as plants. But fungi differ from plants in many ways. One difference is that fungi are non–green (lack chloroplasts and chlorophyll) and so cannot make their own food. Like the plants, however, they possess cell walls. The fungi are more closely related to animals than plants, yet the discipline of biology devoted to the study of fungi, known as mycology, often falls under a branch of botany.