Types of hydrides
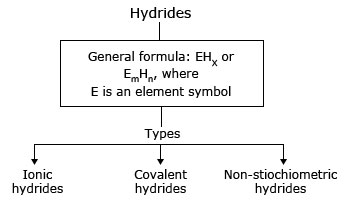
| Ionic hydrides | Covalent hydrides | Non-stiochiometric hydrides | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Other names | Stiochiometric or saline hydrides | Molecular hydrides | Interstitial or metallic hydrides |
| Bonded elements belong to | s-block | p-block | d and f-blocks |
| Properties | Crystalline, non-volatile and non-conductive in solid state | Volatile and covalent | Conductors, catalyst and reductant properties |
| Examples | LiH, BeH2, etc. | HF, H2O, NH3, CH4, B2H6, etc. | LaH2.87, ZrH1.75, etc. |
| Special property | React violently with water | It is reclassified into 3 types as:
i. Electron deficient hydrides that act as Lewis acids. Example: B2H6. ii. Electron precise hydrides that have tetrahedron geometry. Example: CH4 iii. Electron rich hydrides that act as Lewis bases. Example: NH3 |
Some of these metals stores hydrogen in their interstitial spaces. This property makes the compounds as a good source of energy |