Temperature Dependence of Resistivity
The resistivity of a material is temperature dependent. The variation in resistivity for different materials is also different. For example, the resistivity of metals, semiconductors and superconductors varies as shown in the graphs below.
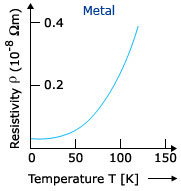
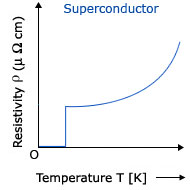
Let a conductor has resistance R0, at the temperature
T0 = 0°C
Then the resistance of the conductor at temperature T°C be Rt
Then the change in temperature ΔT = T°C – T0°C
Change in resistance ΔR = Rt – R0
The change in resistance ΔR depends upon the following factors
- Directly on the initial resistance
- Directly on raise of temperature
- On the nature of material by which the conductor is made up of.
Rt – R0 ∝ R0 × ΔT
Rt – R0 = α R0ΔT
α represents temperature coefficient of resistivity
Rt = R0
+ α × R0ΔT
∴ Rt = R0[1 + α(T - T0)]
But Rt = ρt l/A and R0 = ρ0l/A
Substitute the Rt and R0 in the Rt equation
| ∴ ρ t l/A | = | ρ0l/A[1 + α(T - T0)] |
| ρt | = | ρ0[1 + α(T - T0)] |