Bond between amino acids
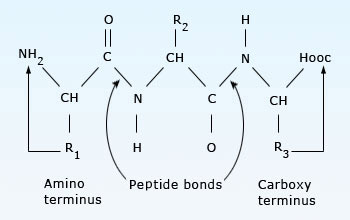 Two ends of a polypeptide chain
A polypeptide is a long, continuous, and unbranched peptide chain.
Two ends of a polypeptide chain
A polypeptide is a long, continuous, and unbranched peptide chain.
A protein consists of a polypeptide backbone with attached side chains. Each type of protein differs in its sequence and number of amino acids; therefore, it is the sequence of the chemically different side chains.
The two ends of a polypeptide chain are chemically different: the end carrying the free amino group (NH3+ , also written NH2) is the amino terminus, or N−terminus, and that carrying the free carboxyl group (COO − , also written COOH) is the carboxyl terminus or C−terminus.
The amino acid sequence of a protein is always presented in the N−to−C direction, reading from left to right.