Hyperbolic functions of complex numbers
The exponential function can be defined for any complex argument. So we can extend the definitions of the hyperbolic
functions to complex arguments also.
The Euler's formula for complex numbers is :
| eix | = | cos x + i sin x |
| Substituting i | = | – i, we have |
| e– ix | = | cos x – i sin x |
| cosh(ix) | = | 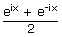 ... by definition
... by definition |
| = | cos x ... from Euler's formulae above | |
| sinh(ix) | = | 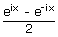 = i sin x
= i sin x |
| ∴ We have | ||
| I. a) cosh (ix) | = | cos x |
| b) sinh (ix) | = | i sin x |
| c) tanh(ix) | = | i tan x |
| II. a) cosh(x + iy) | = | cosh x . cosy + i sinh x . sin y |
| b) sinh(x + iy) | = | sinh x . cosy + i cosh x . sin y |
| III. a) cosh x | = | cos(ix) |
| b) sinh x | = | – i sin(ix) |
| c) tanh x | = | – i tan(ix) |
The above are the relations between hyperbolic functions and ordinary trigonometric functions.
The hyperbolic functions are periodic w.r.t. the imaginary component with period 2πi for
sinh, cosh, sech & cosech; and with period πi for tanh and coth.
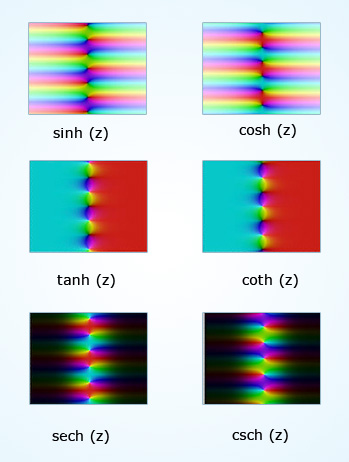
Hyperbolic functions in the complex plane
z representing a complex number, the functions sinh z and cosh z are said to be holomorphic or analytic(see below figures).