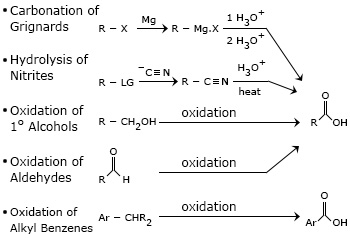
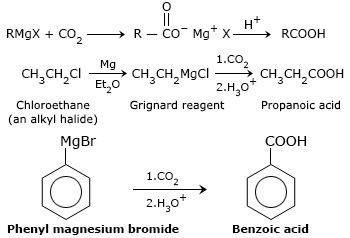
Carbonation of Grignard Reagents(RMgX):
Gregnard reagent reacts with CO2 and gives magnesium carboxylate which on acidification gives a carboxylic acid.
Note: There is an increase in the number of carbon atoms from the alkyl halide to the carboxylic acid. Chlorethane gives propanoic acid.
Hydrolysis of Nitriles :
Acidic hydrolysis:
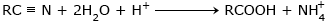
Basic hydrolysis:
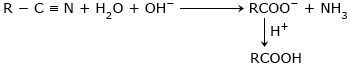
Hydrolysis of carboxylic acid derivatives:
Reaction of acyl halides with water occurs rapidly, and does not require heating or catalysts. Amides, on the other hand, react with water only in the presence of strong acid or base catalysts and external heating.
Acyl halide: Reacts instantly, even with cold water to form the carboxylic acid.
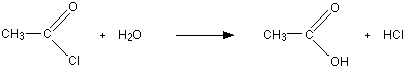
Acid anhydride: Hydrolysis of these compounds occurs at a slow rate and requires heating or boiling with water.
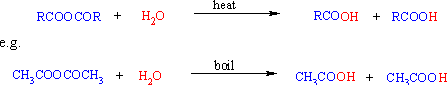
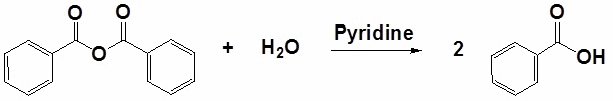
Ester: Hydrolysis occurs on heating with aqueous acid or base.
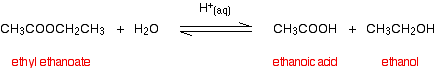
Amide: Amides are the least reactive of the neutral carboxylic acid derivatives.