Examples
Ex1:
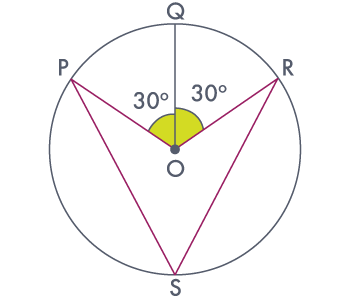
P, Q and R are three points on a circle with centre O such that
∠POQ = 30° and ∠QOR = 30°. If S is a point on the circle other than the
arc PQR, find ∠PSR.
Sol:
| From the given figure | ||
| ∠POR | = | ∠POQ + ∠QOR |
| = | 30° + 30° | |
| = | 60° | |
We know that angle subtended by an arc at the centre is double the angle
subtended by it any point on the remaining part of the circle.
∠PSR = 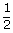 ∠POR =
∠POR =
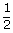 (60°)
= 30°
(60°)
= 30°
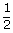 ∠POR =
∠POR =
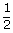 (60°)
= 30°
(60°)
= 30°
Ex2:
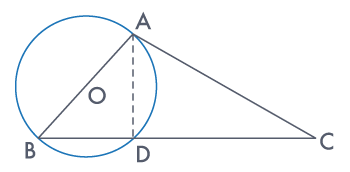
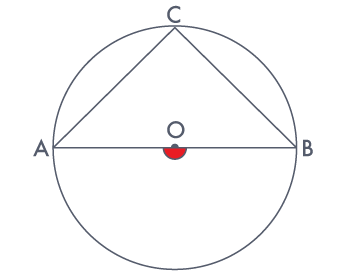
A chord of a circle is equal to the radius of the circle. find
the angle subtended by the chord at a point on the minor arc and also at a point on the
major arc.
Sol:
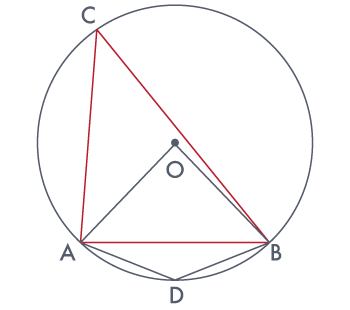
In ΔOAB,
AB = OA = OB = radius
∴ ΔOAB is an equilateral triangle.
Therefore, each interior angle of this triangle will be of 60°
∴ ∠AOB = 60°
∠ACB = 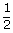 ∠AOB =
∠AOB =
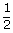 (60°)
= 30°
(60°)
= 30°
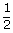 ∠AOB =
∠AOB =
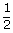 (60°)
= 30°
(60°)
= 30°
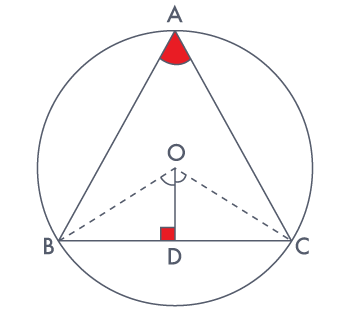
In cyclic quadrilateral ACBD,
∠ACB + ∠ADB = 180deg; (opposite angle in cyclic quadrilateral)
∴ ∠ADB = 180° – 30° = 150°
Therefore, angle subtended by this chord at a point on the major arc and the minor arc are
30° and 150° respectively.
 at O = 2 ×
angle
formed by it at C].
at O = 2 ×
angle
formed by it at C].