Young's modulus [ Y or E] :
Consider a wire of length 'L' and uniform area of cross-section 'A'. Let 'F' be a force acting on a length of the wire an 'Δl' be the increase in length. Within the elastic limit, the ratio of longitudinal stress to the longitudinal stain is called 'Young's modulus' of the material of the wire.
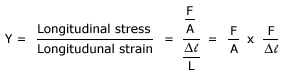
S.I. unit of 'Y' is 'Nm-2' or 'Pascal';
C.G.S. unit is 'dyne cm-2'
Bulk modulus (B or K) :
Consider a sphere or a cube of volume 'V'. Let 'F' be the force acting normally and uniformly over the surface area A. Since the force is normal, 'F/A' is called 'pressure'. Under this pressure the volume of the body decreases by 'Δv'.
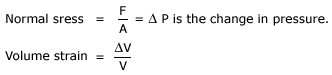
Within the elastic limit, ratio of normal stress to volume strain is a constant and is called 'bulk modulus' of elasticity,denoted bu B (or K).
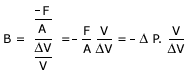
-ve sign shows that as pressure is increased, the volume is decreased. The reciprocal of bulk modulus is called compressibility.
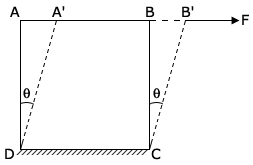
Rigid Modulus (G or n) or shear modulus :
Within the elastic limit the ratio of tangential stress to shearing strain is called rigid modulus. Denoted by G (or n).
Let 'F' be the tangential stress applied to the upper face of a cube, whose lower face is fixed. Surface area is 'A'. Let 'θ' be the angle of shear.