Examples
Ex 1:
Convert 16%, 37.5% and 250% into fractions?
Sol:
To convert 16% into a fraction we have to divide it by 100.
| ∴ 16% | = | 16 / 100 |
| = | (4 × 4) / (4 × 25) | |
| = | 4 / 25 |
To convert 37.5% into a fraction we have to divide it with 100
| ∴ 37.5% | = | 37.5 / 100 |
Multiply the numerator and denominator by 10 to remove the decimal.
| ⇒ 37.5% | = | 375 / 1000 |
| = | (125 × 3) / (125 × 8) | |
| = | 3 / 8 |
To convert 250% into a fraction, we have to divide it by 100.
| ∴ 250% | = | 250 / 100 |
| = | (5 × 50) / (2 × 50) | |
| = | 5 / 2 |
Ex 2:
(i) If 9.5% of a number is 76, find the number.
(ii) Increase the number 240 by 15%.
(iii) Decrease the number 275 by 8%.
Sol:
(i) Let the required number be x.
According to the given condition:
9.5% of x = 76.
9.5% of x = 76.
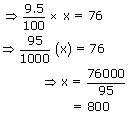
Hence required number = 800.
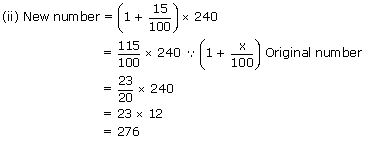
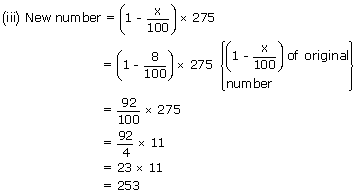
Ex 3:
On reducing the price of a shirt by 8%, it becomes Rs. 423.20. What was its original price?
Sol:
Let the original price of the shirt be Rs. x.
Since the price has been reduced by 8%, we get
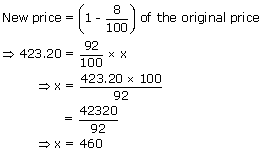
Hence, the original price of the shirt is Rs. 460.
Ex 4:
A number is increased by 20% and then decreased by 20%. Find the net increase or decrease
per cent?
Sol:
Let the given number be x.

Hence, net decrease per cent = 4%.
Ex 5:
Swathi spends 65% of her salary and the rest she saves. If she saves Rs. 2940 per month, what is
her monthly salary?
Sol:
Let the monthly salary be Rs. x.
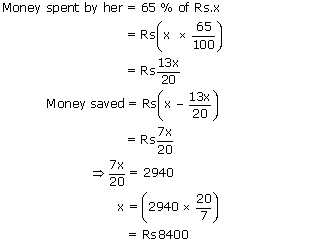
∴ Swathi's monthly salary = Rs. 8400.
Ex 6:
In an examination, one requires 40% marks to pass, Rahul gets 185 marks and fails by 15 marks.
What are the maximum marks?
Sol:
Let the maximum marks be x.
| Pass marks | = | (185 + 15) |
| = | 200 | |
| ∴ 40% of x | = | 200 |
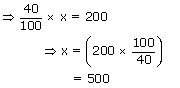
Hence, maximum marks = 500.
Ex 7:
The price of sugar goes up by 20%. By how much per cent must a housewife reduce her consumption
of sugar so that the expenditure on sugar remains the same?
Sol:
Let the consumption of sugar originally be 1 unit and let its cost be Rs. 100.
New cost of 1 unit = Rs. 120.
Now, Rs. 120 yield 1 unit of sugar.
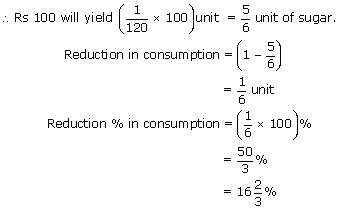
Ex 8:
Out of her total monthly salary, Mrs. Gupta spends 20% on house rent and 60% of the rest
on household expenditure. If she saves Rs. 2800, what is her total monthly salary?
Sol:
Let the total monthly salary of Mrs. Gupta be Rs. x.
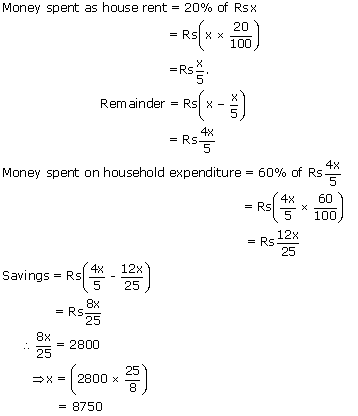
Hence, the total monthly salary of Mrs. Gupta is Rs. 8750.
Ex 9:
The population of a town increases by 6% annually. If the present population is 17490, what was
it a year ago?
Sol:
Let the population of the town a year ago be x.
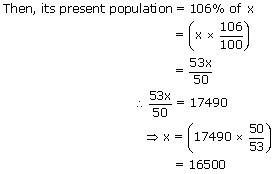
Hence, the population of the town a year ago was 16500.
Ex 10:
The value of a machine depreciates every year by 10%. If the present value of x be Rs. 99000,
what
was its value last year?
Sol:
Let the value of the machine last year be Rs. x.
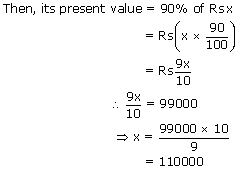
∴ Value of the machine last year = Rs. 110000.
Ex 11:
A's income is 60% more than that of B. By what per cent is B's income less ?
Sol:
Let B's income be Rs. 100.
| Then, A's income | = | Rs. 160. |
| If A's income is Rs. 160, then B's income | = | Rs. 100 |
| If A's income is Rs. 100, then B's income | = | Rs. (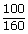 × 100) × 100) |
| = | Rs. 62.50. | |
| ∴ B's income is less than A's income by (100 – 62.50 ) | = | 37.5 % |