 Centrifugation
Centrifugation
All biochemical tests come under chemical pathology. These are performed on any kind of body fluid, but mostly on serum or plasma.
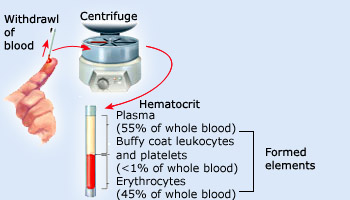
Serum is the yellow watery part of blood that is left after blood has been allowed to clot and all blood cells have been removed. This is most easily done by centrifugation, which packs the denser blood cells and platelets to the bottom of the centrifuge tube, leaving the liquid serum fraction resting above the packed cells. This initial step before analysis has recently been included in instruments that operate on the "integrated system" principle.
Plasma is in essence the same as serum, but is obtained by centrifuging the blood without clotting. Plasma is obtained by centrifugation before clotting occurs. The type of test required dictates what type of sample is used. Thus, centrifugation is a process that involves the use of the centrifugal force for the sedimentation of mixtures with a centrifuge, used in industry and in laboratory settings.