An energy wave transmitted by a transmitter antenna is called radio wave. It is a complex form of energy containing both electric and magnetic fields. As such radio waves are also called as EM waves or radiation. Like the light and heat waves, these can be reflected, refracted and diffracted in the atmosphere.
The basic shape of the wave generated by a transmitter is a sine wave. However, once radiated into the space, it may not retain the characteristics of the sine wave in total. There is bound to be distortion.
Radiowaves are often referred to by their wavelength(in meters) rather than by frequency(in Hertz). A wavelength is the space occupied by one full cycle of a radio wave at a given time. The frequency and wavelength are related by,
Frequency(f) = 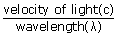
In the EM spectrum, the frequencies in the range 3KHz to 300GHz are called Radio Frequencies(RF) as they are commonly uses in radio communications.
This part of the RF spectrum(3KHz - 300GHz) is divided into bands. Each band is 10 times higher in frequency than the one immediately below it.
(The RF bands are listed in the table earlier).