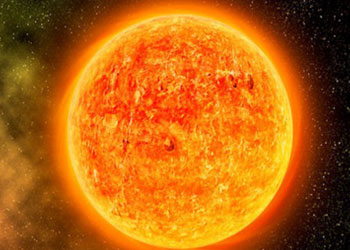
 Plasma occurs in the stars, including the Sun. Inside the Sun, temperature is so high that the constituent Hydrogen and Helium molecules break their bonds and gives free electrons. As a result, electrically charged particles called ions are generated. The mixture of free electrons and ions gives plasma which is responsible for the glow. It is characterized by a complexity that is not exhibited by a solid, liquid and gaseous state.
Plasma occurs in the stars, including the Sun. Inside the Sun, temperature is so high that the constituent Hydrogen and Helium molecules break their bonds and gives free electrons. As a result, electrically charged particles called ions are generated. The mixture of free electrons and ions gives plasma which is responsible for the glow. It is characterized by a complexity that is not exhibited by a solid, liquid and gaseous state.
One may wonder that the primary states of matter contribute to minor part of the Universe, while a major portion is composed of plasma. Plasma contains ionized gases and can exist at extremely high temperature (105 K). Plasma, like gas, does not have definite shape or volume. It can generate electromagnetic forces and can be accelerated. It provides many practical uses, new technologies, consumer products and also promises for abundant energy.
Plasma can also be made on the earth by passing electricity through gases at very low pressures taken in a glass tube (called discharge tube). The fluorescent tubes and neon sign bulbs form plasma when they are switched on. A fluorescent tube may contain helium gas (or some other gas), and a neon sign bulb contains neon gas. When electricity is passed through a fluorescent tube (or neon sign bulb) it glows.
In 1920, an Indian scientist Satyendra Nath Bose calculated for the fifth state of matter. On the basis of these calculations, Albert Einstein predicted the existence of a new state of matter called Bose–Einstein Condensate (BEC). This fifth state of matter was finally achieved by three USA Scientists: Cornell, Ketterle and Wieman. They cooled a gas of extremely low density (about one hundred thousandth the density of normal air) to super low temperature (<10– 7 K).