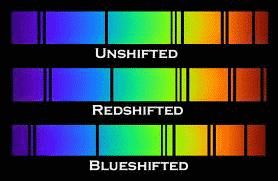
 Radiation is redshifted when its wavelength increases, and is blueshifted when its wavelength decreases.
Radiation is redshifted when its wavelength increases, and is blueshifted when its wavelength decreases.
When wave energy like sound or radio waves travels from two objects, the wavelength can seem to be changed if one or both of them are moving. This is called the Doppler effect.
The Doppler effect causes the received frequency of a source (how it is perceived when it gets to its destination) to differ from the sent frequency if there is motion that is increasing or decreasing the distance between the source and the receiver. This effect is readily observed as the variation in the pitch of sound always occurs between a moving source and a stationary observer.
When the distance between the source and receiver (of electromagnetic waves) remains constant, the frequency wave is the same in both places. When the distance between the source and receiver (of electromagnetic waves) is increasing, the frequency of the received wave forms is lower than the frequency of the source wave form. When the distance is decreasing, the frequency of the received wave form will be higher than the source wave form.
Besides sound and radio waves, the Doppler effect also affects the light emitted by other bodies in space. If a body in space is “blue shifted”, its light waves are compacted and it is coming towards us. If it is “red shifted” the light waves are spread apart, and it is traveling away from us. All other stars we have detected are “red shifted,” which is one piece of evidence for the theory that the universe is constantly expanding, perhaps from a “big bang”.