
A solution is a homogeneous mixture (mixture is just the same throughout) of one substance dissolved in another so the properties are the same throughout. A solution is composed of a solute and the solvent. Solutions typically occur by the solute being dissolved into the solvent. The substance which is dissolved in a liquid to make a solution is called solute. The liquid in which solute is dissolved is known as solvent.
Types of solutions:
- Suspensions
- Colloids
- True solutions
Suspensions: A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture in which the small particles of a solid are spread throughout a liquid without dissolving in it. E.g.: Chalk water mixture (suspension of fine chalk particles suspended in water), muddy water (suspension of soil particles in water), milk of magnesia (magnesium hydroxide in water), sand particles suspended in water, and flour in water.
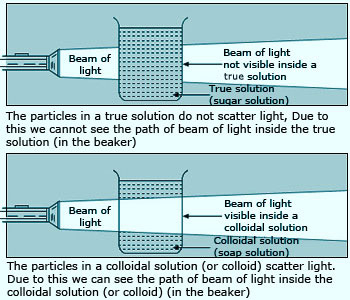
Colloids: A colloid is a kind of solution in which the size of solute particles is intermediate between those in true solutions and those in suspensions. Though colloids appear to be homogeneous, but actually they are found to be heterogeneous when observed through a high power microscope. So, a colloid is not a true solution. E.g.: Soap solution, starch solution, milk, ink, blood, jelly and solutions of synthetic detergents.
The scattering of light by colloidal particles is known as Tyndall effect.
The scattering of light by colloidal solutions tells us that the colloidal particles are much bigger than the particles of a true solution and hence colloidal solutions are not true solutions. So, a true solution can be distinguished from a colloidal solution by the fact that a true solution does not scatter a beam of light passing through it but a colloidal solution does not show Tyndall effect but a colloidal solution shows Tyndall effect.
| Technical name of contents | Dispersed phase | Dispersion phase | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sol | Solid | Liquid | Ink, soap solution, starch solution, most paints |
| Solid sol | Solid | Solid | Colored gemstones like ruby |
| Aerosol | a. Solid b. Liquid |
Gas Gas |
Smoke, automobile exhausts, hairspray, fog, mist, clouds |
| Emulsion | Liquid | Liquid | Milk, butter, face cream |
| Foam | Gas | Liquid | Fire–extinguisher foam, soap bubbles, shaving cream, beer foam |
| Solid foam | Gas | Solid | Insulating foam, foam rubber, sponge, bread |
| Gel | Solid | Liquid | Jellies, gelatin, hair gel |
Solubility is a measure of the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent to form a stable solution. Different solutes have different solubility (S) and are expressed in terms of grams per milliliter (g/mL). For example, for sodium chloride (NaCl), solubility (S) = 39.12g/100mL, water at 100�C. Whereas for silver chloride (AgCl), solubility (S) = 0.00021g/ 100mL, water at 100°C.
Although solubility has a quantitative meaning, depending on the relative amounts of solute, solutions are described as – concentrated solutions, dilute solutions, saturated solutions, supersaturated solutions and unsaturated solutions.
- Concentrated solutions: If a solution contains large amount of solute dissolved in a given solvent, then the solution is said to be a concentrated solution.
- Dilute solutions: If a solution contains small amount of solute dissolved in a given solvent, then the solution is said to be a dilute solution.
- Saturated solutions: If a solution contains maximum amount of solute dissolved in a given solvent, then the solution is said to be a saturated solution and the solution is in equilibrium with un–dissolved solute. i.e., the solution contains un–dissolved solute.
- Supersaturated solutions: If a solution contains more than the maximum amount of solute dissolved in a given solvent, then the solution is said to be a supersaturated solution. But these supersaturated solutions are meta–stable, that is the solute gets crystallized on shaking the solution or by adding a seed crystal.
- Unsaturated solutions: If a solution contains less than the maximum amount of solute dissolved in a given solvent then the solution is said to be an unsaturated solution. The solution does not contain any un–dissolved solute.