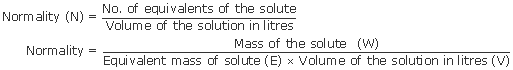Normality(N)
States of Matter > Solutions
 Normality of different compounds
Normality of different compounds
| Formula of Compound | Formula weight | Equivalent weight | Concentration | Volumes that react |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCl | 36.5 | 36.5 | 1N | 1L |
| NaOH | 40 | 40 | 1N | 1L |
| H2SO4 | 98 | 49 | 1N | 1L |
Normality is the a way of expressing the concentration of a solution. It is denoted by letter “N”.
It is similar to molarity in many ways. The difference is that molarity provides the information about the number of molecules in a liter of solution and normality provides information about the number of reactive units in a liter of solution.
Molarity is expressed in terms of moles of a compound per liter of solution whereas the normality is expressed in equivalents per liter. An equivalent can be defined as the number of moles of “reactive units” in a compound. One equivalent can either react with or take the place of one mole of hydrogen ions.
Normality is the only concentration unit that is dependent on the reaction process.