 Magnesium metal burns with bright white light on exposure to fire in air.
Magnesium metal burns with bright white light on exposure to fire in air.
 Magnesium chloride as a natural mineral can be obtained from sea beds.
Magnesium chloride as a natural mineral can be obtained from sea beds.
Magnesium is a IIA group, alkaline earth metal. Discovered by sir Humphry davy. Magnesium is a strong, silvery–white, light–weight, highly flammable metal. Magnesium metal burns with bright white light on exposure to fire in air.
Compounds of Magnesium:[Most of the magnesium compounds are water soluble white crystals.]
Magnesium chloride[MgCl2.xH2O]
MgCl2 and its various hydrates MgCl2(H2O)x are called as magnesium chloride. The hydrated magnesium chloride can be extracted from brine or sea water. Magnesium chloride as the natural mineral can be extracted from ancient sea beds and it also occurs in mineral carnallite. Magnesium metal is obtained on a large scale from anhydrous magnesium chloride.
 Magnesium chloride a white crystalline solid.
Magnesium chloride a white crystalline solid.
Preparation:
In the laboratory, magnesium chloride is prepared by the action of hydrochloric acid on magnesium oxide or magnesium carbonate.
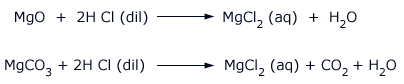
The solution on concentrating and cooling gives crystals of MgCl2.6H2O.
On industrial scale, magnesium chloride is prepared from sea water. The sea water on treatment with lime gives precipitate of magnesium hydroxide. The precipitate is separated and dissolved in hydrochloric acid. The solution upon crystallization and cooling gives crystals of MgCl2.6H2O.
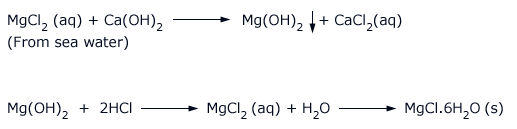
Magnesium chloride is also obtained from carnallite (KCl.MgCl2.6H2O). The ore is powdered and boiled with water for some time. On cooling, KCl crystallizes out and magnesium chloride being more soluble, remains in the mother liquor. The mother liquor is concentrated and on cooling gives crystals of MgCl2. 6H2O.
 Magnesia cement used in tiles
Magnesia cement used in tiles
Properties of magnesium chloride hexahydrate:
Magnesium chloride hexahydrate is a white crystalline solid and is deliquescent. It decomposes on heating to give magnesium oxide.
When heated in a current of dry hydrogen chloride gas it gives anhydrous salt. A saturated solution of this salt when mixed with
magnesium oxide, sets to a hard mass with the formula MgCl2.5MgO.xH2O. The hard mass is known as magnesia
cement or sorel cement.

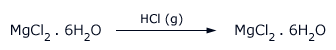
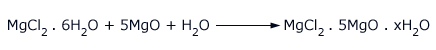
Uses:
- Magnesium chloride is used for the manufacture of magnesia cement which resembles marble and is used for making tiles.
- It is used in the preparation of magnesium by electrolytic method.
 Magnesite a natural magnesium carbonate mineral
Magnesite a natural magnesium carbonate mineral
Magnesium Carbonate(MgCO3)
Most common magnesium carbonate forms are magnesite(anhydride MgCO3) and di, tri, pentahydrates.
Some basic forms of magnesium carbonate such as Artinite (MgCO3.Mg(OH)2.3H2O), Hydro magnesite (4MgCO3.Mg(OH)2.4H2) and Dypingite ocurs as minerals.
 An amorphous magnesium carbonate
An amorphous magnesium carbonate
Preparation and properties:
Magnesium carbonate is ordinarily obtained by mining the magnesite mineral.
MgCO3.3H2O, trihydrate salt can be prepared by mixing solutions of magnesium and carbonate ions under the
atmosphere of CO2.
 MgCO3 +
CO2↑ + H2O
MgCO3 +
CO2↑ + H2OFollowing the filteration of solution, the filtrate is dried under vacuum to produce magnesium carbonate as a hydrated salt.
Magnesium carbonate on reaction with acids decomposes with the release of CO2.
Reaction with acid:
 MgCl2↓ +
CO2↑ + H2O
MgCl2↓ +
CO2↑ + H2O MgSO4↓ + CO2↑ + H2O
MgSO4↓ + CO2↑ + H2O On heating between the temperatures of 250°C to 800°C, MgCO3 decomposes leaving MgO and CO2 with the reaction enthalpy of 118 kJ/mole. This process is called calcination.
 MgO + CO2↑
MgO + CO2↑  Magnesium carbonate used as an antiacid
Antiacids are the substances which neutralizes the stomach acidity
Magnesium carbonate used as an antiacid
Antiacids are the substances which neutralizes the stomach acidity
Uses:
- MgCO3 is used in flooring, fire proofing, fire extinguishing compositions, cosmetics, dusting powder and tooth pastes.
- It is used as a filler material, smoke suppressant in plastics, a reinforcing agent in neoprene rubber, as a drying agent, laxative and in color retention in foods.
- High purity magnesium carbonate is used as an antacid.
- As it is insoluble in water it is added as an additive in table salt to keep it free flowing.
- It is used as clay in the preparation of face masks.