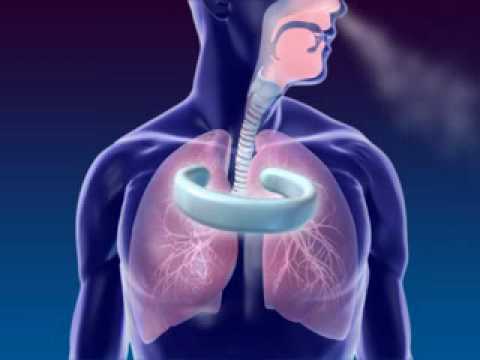
 Human respiratory system
Breathing, or pulmonary ventilation, describes the process of inhaling and exhaling air. The human respiratory system consists of the respiratory tract and the lungs.
Human respiratory system
Breathing, or pulmonary ventilation, describes the process of inhaling and exhaling air. The human respiratory system consists of the respiratory tract and the lungs.
The Respiratory System is crucial to every human being. Without it, we would cease to live outside of the womb. Let us begin by taking a look at the structure of the respiratory system and how vital it is to life. During inhalation or exhalation air is pulled towards or away from the lungs, by several cavities, tubes and openings. Respiration is the process by which living organisms take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide. The human respiratory system, working in conjunction with the circulatory system, supplies oxygen to the body's cells, removing carbon dioxide in the process. The exchange of these gases occurs across cell membranes both in the lungs (external respiration) and in the body tissues (internal respiration). Breathing or pulmonary ventilation, describes the process of inhaling and exhaling air. The human respiratory system consists of the respiratory tract and the lungs.
The respiratory system, also referred as ventilatory system in the biological system that introduces respiratory gases to the interior and performs gas exchange. In humans and other mammals, the anatomical features of the respiratory system include airways, lungs, and the respiratory muscles. Molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide are passively exchanged, by diffusion, between the gaseous external environment and the blood. This exchange process occurs in the alveolar region of the lungs.
Simply put, Breathing starts at the nose and mouth. You inhale air into your nose or mouth, and it travels down the back of your throat and into your windpipe, or trachea. Your trachea then divides into air passages called bronchial tubes. The organs of the respiratory system make sure that oxygen enters our bodies and carbon dioxide leaves our bodies. As air moves along the respiratory tract it is warmed, moistened and filtered. Gas exchange in the lungs and in the alveoli is between the alveolar air and the blood in the pulmonary capillaries. This exchange is a result of increased concentration of oxygen, and a decrease of C02. This process of exchange is done through diffusion.