 Illustration of gaseous exchange phenomenon in lungs
Illustration of gaseous exchange phenomenon in lungs
 The first step to obtaining nutrition is ingestion, a process where food is taken in through the mouth and broken down by teeth and saliva.
The first step to obtaining nutrition is ingestion, a process where food is taken in through the mouth and broken down by teeth and saliva.
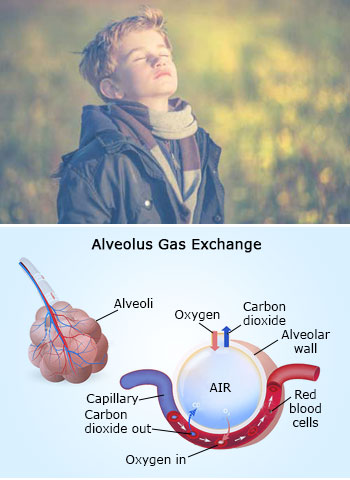
The upper respiratory system carries air between the nose and the lungs during breathing. Air passes through a system of passages consisting of the pharynx (also part of the digestive tract), the larynx (voice box), the trachea, two bronchi (one bronchus to each lung) and a large number of bronchial passages. These end in alveoli, millions of tiny air sacs in each lung. They are surrounded by a network of tiny capillaries and are the sites where vital gas exchange between the lungs and the blood takes place.
Nitrogen, which makes up about 80% of atmospheric air, is breathed in and out, but it cannot be used by the body in gaseous form. The nitrogen needed by the body is obtained by eating protein-containing foods, mainly meat and fish.
Ingestion of nutrients
Digestion : The food we take is chemically complex hence the digestive system evolved . Its main function is to break down into smaller particles, or digest, food so that it can be absorbed into the circulation and then used by body cells. The digestive system consists of the alimentary canal and accessory glands.
The alimentary canal is essentially a tube that begins at the mouth and continues through the pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, rectum and anus.
Glands : The accessory organs situated outside the alimentary canal with ducts leading into it are the salivary glands, the pancreas and the liver. There are also many tiny glands situated in the walls of the alimentary canal. Most of these glands synthesize digestive enzymes that are involved in the chemical breakdown of food. Some others secrete mucus that provides lubrication.
Metabolism : This is the sum total of the chemical activity in the body. It consists of two groups of processes: Anabolism, building or synthesizing large and complex substances. Catabolism is the process where it involves breaking down substances to provide energy and raw materials for anabolism, and substances for excretion as waste. The sources of energy are mainly the carbohydrates and fats provided by the diet. If these are in short supply, proteins are used.