Important Functions
Biochemistry & Cell Biology > Cell structure
 Chromosomes – Stores DNA
Chromosomes – Stores DNA
Within cells, there is an intricate network of organelles that all have unique functions.
These organelles allow the cell to function properly. Arranged below according to location (nucleus, cytoplasm, and surface) is a description of common organelles.
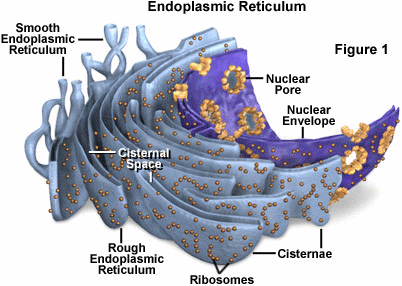 The endoplasmic reticulum manufactures, processes, and transports a wide variety of biochemical compounds.
The endoplasmic reticulum manufactures, processes, and transports a wide variety of biochemical compounds.
Parts of nucleus and its functions:
Chromosomes: Contains genetic information, stores DNA.
Nuclear membrane: Surrounds nucleus and contains numerous openings for nuclear traffic.
Nucleolus: Contains RNA for protein manufacture.
Organelles in cytoplasm and their functions:
- Chloroplast: Performs photosynthesis (only in plant cells)
- Cell wall: For support (only in plant cells)
- Plasma membrane: Outer membrane of cell that controls cellular traffic and protects the cell from harmful circumstances.
- Mitochondria: Make energy out of food. (ATP synthesis).
- Cytoskeleton: Composed of microtubules, Supports cell and provides shape and aids movement of materials in and out of cells.
- Endoplasmic reticulum: Referred as "intracellular highway" because it is for transporting all sorts of items around the cell. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle involved in lipid synthesis, detoxification, and carbohydrate metabolism.
- Golgi apparatus: Make, process and package proteins.
- Ribosomes: Protein synthesis.
- Lysosome: Contains digestive enzymes to help break food down.
- Vacuoles: Used for storage, vacuoles usually contain water or food, (Are you thirsty? Perhaps your vacuoles need some water) and also performs phagocytosis.