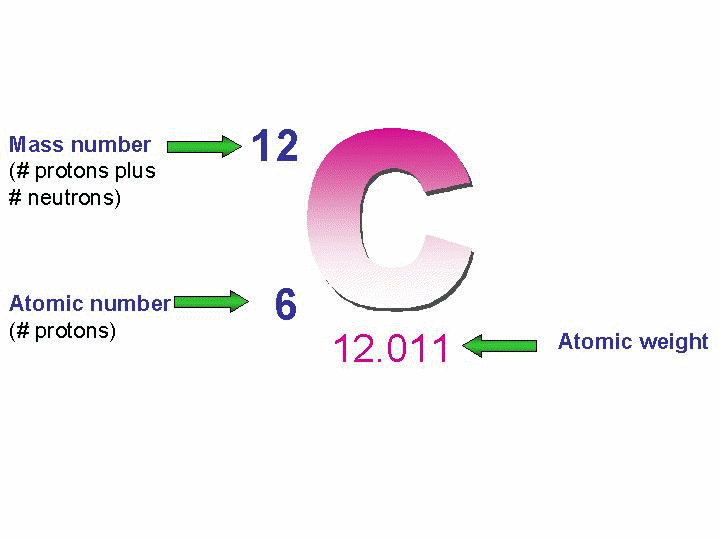
 Atomic number and atomic mass of carbon
The atomic number of an element indicates the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element.
For example, an atom of carbon has 6 protons in its nucleus so its atomic number is 6.
No other element has atoms with 6 protons in their nuclei.
The atomic mass of an element indicates the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom of that element.
Atomic number and atomic mass of carbon
The atomic number of an element indicates the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element.
For example, an atom of carbon has 6 protons in its nucleus so its atomic number is 6.
No other element has atoms with 6 protons in their nuclei.
The atomic mass of an element indicates the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom of that element.
Atomic number
The atomic number (also known as the proton number) is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom and
therefore identical to the charge number of the nucleus. It is conventionally represented by the symbol Z.
The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element.
In an atom of neutral charge, the atomic number is also equal to the number of electrons.
Mass number
The total weight of an atom is called the atomic weight or mass number.
It is approximately equal to the number of protons and neutrons, with a little extra added by the electrons.
Protons and Neutrons are found in the nucleus, a term is needed to define the number of protons and neutrons
(nucleons) in an element.
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is its mass number(A).
Each proton and each neutron contributes one unit to the mass number.
The mass number is a count of the number of particles in an atom's nucleus.
Mass Number = (Number of Protons) + (Number of Neutrons)
Mass number = no. of particles in nucleus
No. of neutrons = Mass number − Atomic number
Atomic number = no. of protons and no. of electrons.